Zero-Copy 简析
使用场景
什么是 Zero-Copy
WIKI定义:
“Zero-copy” describes computer operations in which the CPU does not perform the task of copying data from one memory area to another. This is frequently used to save CPU cycles and memory bandwidth when transmitting a file over a network.
“零拷贝”是指计算机操作的过程中,CPU不需要为数据在内存之间的拷贝消耗资源。通常是指计算机在网络上发送文件时,不需要将文件内容拷贝到用户空间(User Space)而直接在内核空间(Kernel Space)中传输到网络的方式。
Zero-Copy 常用于静态资源从磁盘到网络的发送(中间不对资源进行改变),这在web server提供的功能中很常见,一个例子是:保存在磁盘上的一张图片应某个网络请求被从磁盘中取出并通过socket发送至请求方。
## Zero-Copy 与传统IO方式对比
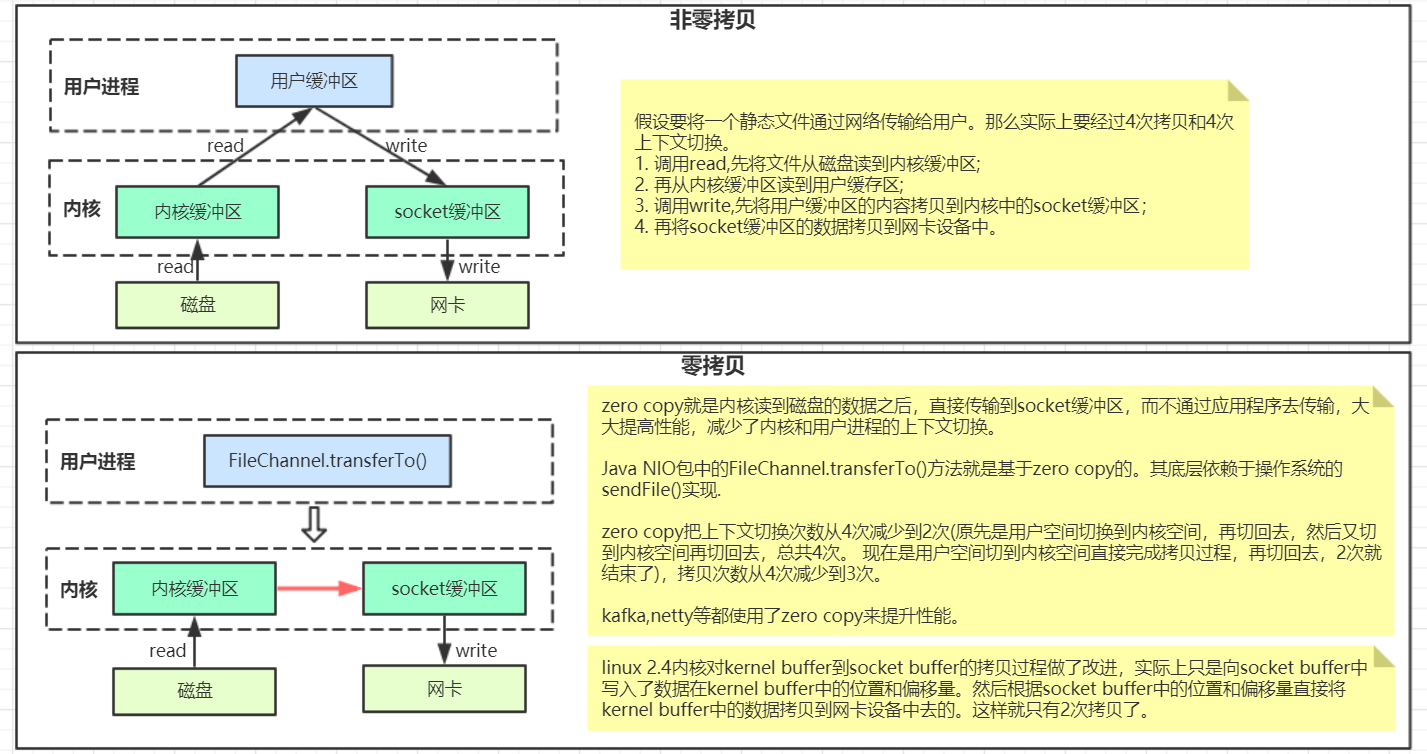
Zero-Copy 是消除了内核空间到用户空间的复制,并不是完全没有发生copy。并不是所有的操作系统都支持这一特性,并且,如果要对文件进行更改,如加密等,Zero-Copy方式也是做不到的。
Java Zero-Copy
FileChannel.transferTo()
磁盘上的文件,直接写到一个可写的SocketChannel,除了内核空间到用户空间的复制。例如:
SocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT);
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(socketAddress);
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(file).getChannel();
fileChannel.transferTo(0, file.length(), socketChannel);
//channel write/read....
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
下面使用Java nio写一个例子,Server直接将磁盘上的一个文件通过Zero-Copy方式发往客户端:
Server:
public class SelectorServer {
private final static int DEFAULT_PORT = 9999;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = DEFAULT_PORT;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}
System.out.println("Server starting ... listening on port " + port);
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector s = Selector.open();
ssc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
for (;;){
int n = s.select();
if (n == 0) {
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = s.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc;
sc = ((ServerSocketChannel) key.channel()).accept();
if (sc == null) {
continue;
}
System.out.println("Receiving connection");
File file = new File("./file/1.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(file).getChannel();
fileChannel.transferTo(0, file.length(), sc);
sc.close();
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
Client:
public class SelectorClient {
private final static int DEFAULT_PORT = 9999;
private static ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = DEFAULT_PORT;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}
try {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", port);
sc.connect(addr);
while (sc.read(bb) != -1) {
bb.flip();
}
Charset charset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
System.out.println(charset.decode(bb).toString());
bb.clear();
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DirectBuffer
DirectBuffer,堆外内存。在上面的例子中已经用到了,我们把channel的接受读到了一个DirectBuffer中,使用方式:
ByteBuffer directByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
这种方式是直接在堆外分配一个内存,不需要堆内内存和堆外内存数据拷贝的操作。
« AQS源码解析
超细致 ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池源码解析 »